Excitation Coil Model¶
Introduction¶
Excitation coils are widely used in electromagnetic devices such as motors, transformers, and inductors. They generate magnetic fields by driving electric current through conductors.
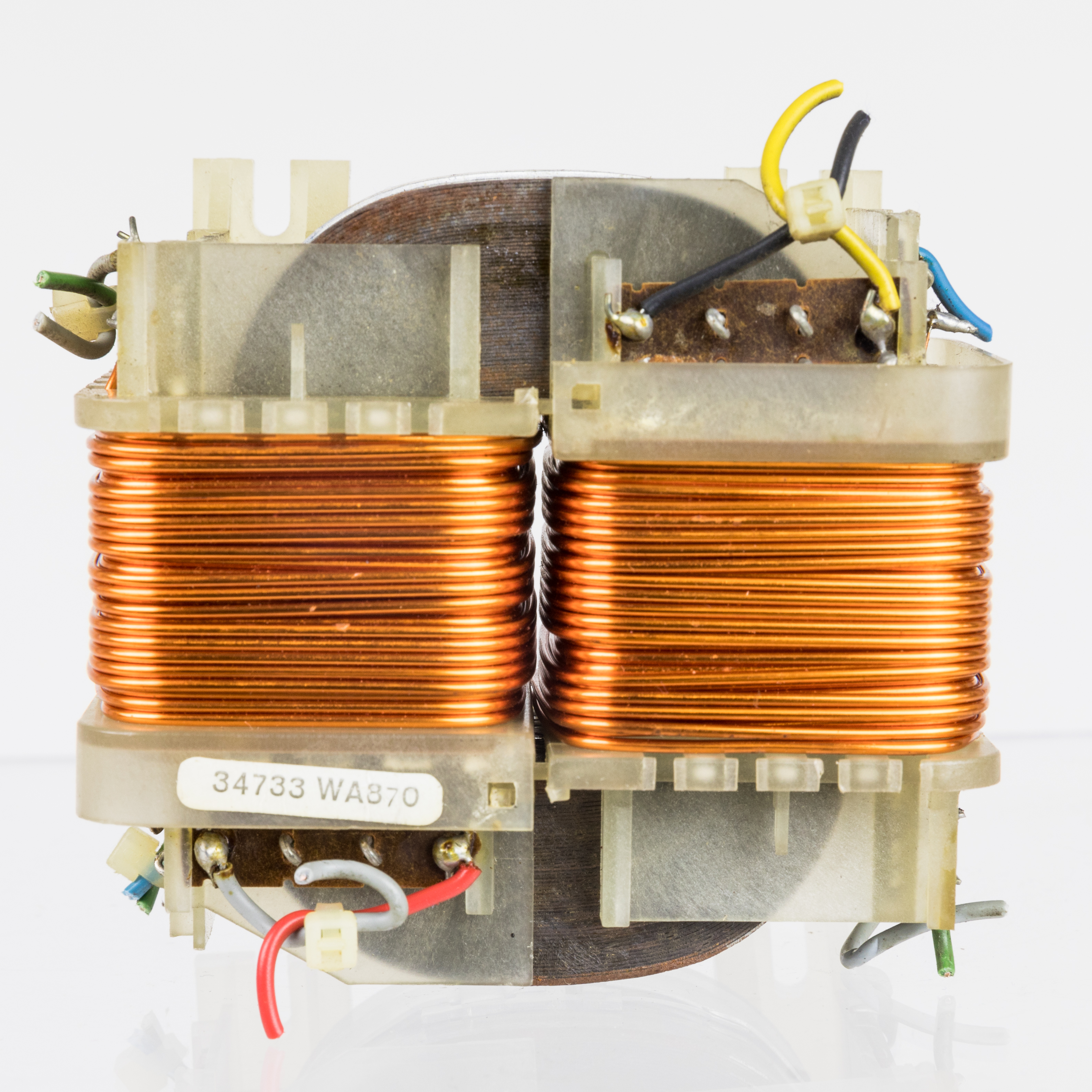
|
| A transformer with a primary and secondary coil. Both coils consist of thin wires wound many times around a magnetic core. (image credit: CC BY-SA 4.0). |
This model allows the definition of different coil geometries, topologies, and excitation types using a unified and physically consistent framework.
To add an excitation coil model to a simulation:
from mufem.electromagnetics.coil import ExcitationCoilModel
coil_model = ExcitationCoilModel()
sim.get_model_manager().add_model(coil_model)
Coil Specification¶
Each coil is described using a CoilSpecification, which defines:
- Name — identifier of the coil
- Marker — the geometric region or boundary to which the coil applies
- Coil type — physical realization of the winding
- Coil topology — whether terminals are open or closed
- Coil excitation — how the coil is electrically driven
All of these are required.
from mufem.electromagnetics.coil import CoilSpecification
coil = CoilSpecification(
name="Coil",
marker=my_coil_marker,
topology=my_coil_topology,
type=my_coil_type,
excitation=my_coil_excitation
)
coil_model.add_coil_specification(coil)
Coil Topology¶
The coil topology specifies how the electrical circuit connects to the coil.
| Name | Description | Illustration |
|---|---|---|
| Open coil | The coil has electrical terminals. Current enters and leaves through designated boundary faces. | 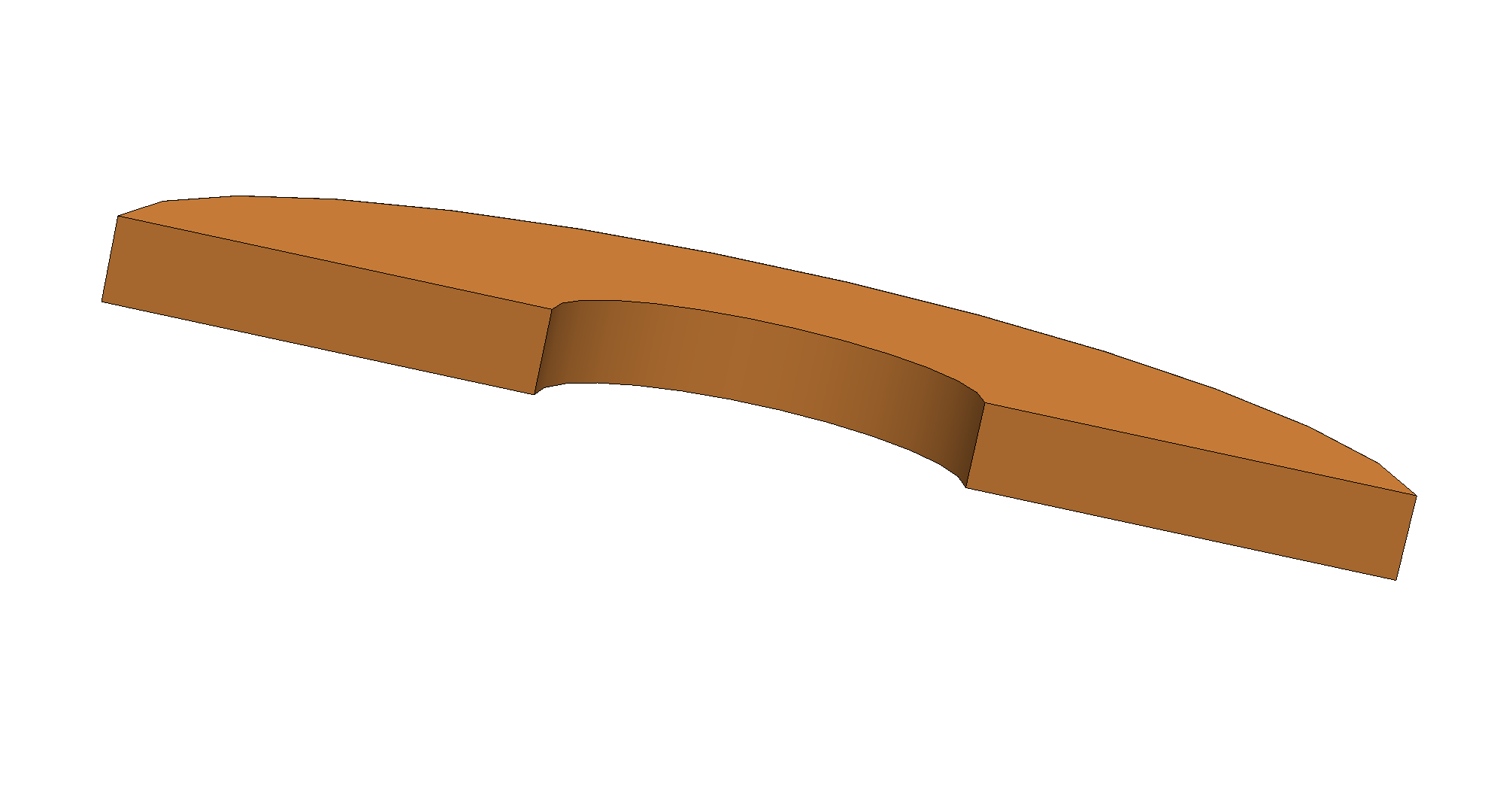 |
| Closed coil | The coil is electrically closed. Current circulates internally without terminals. | 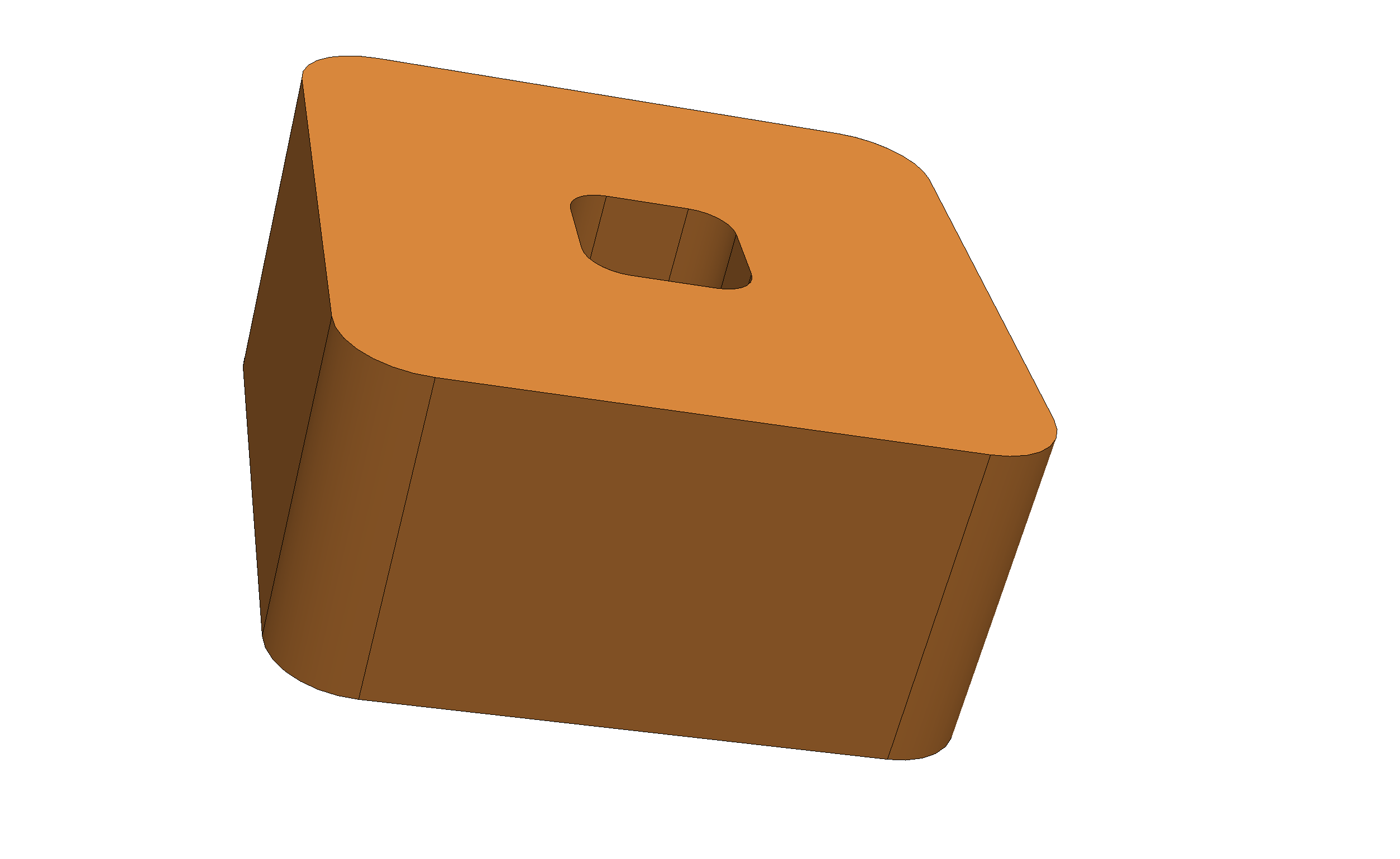 |
Coil Type¶
The coil type defines how the conductor is physically represented.
| Name | Description | Illustration |
|---|---|---|
| Stranded coil |
|
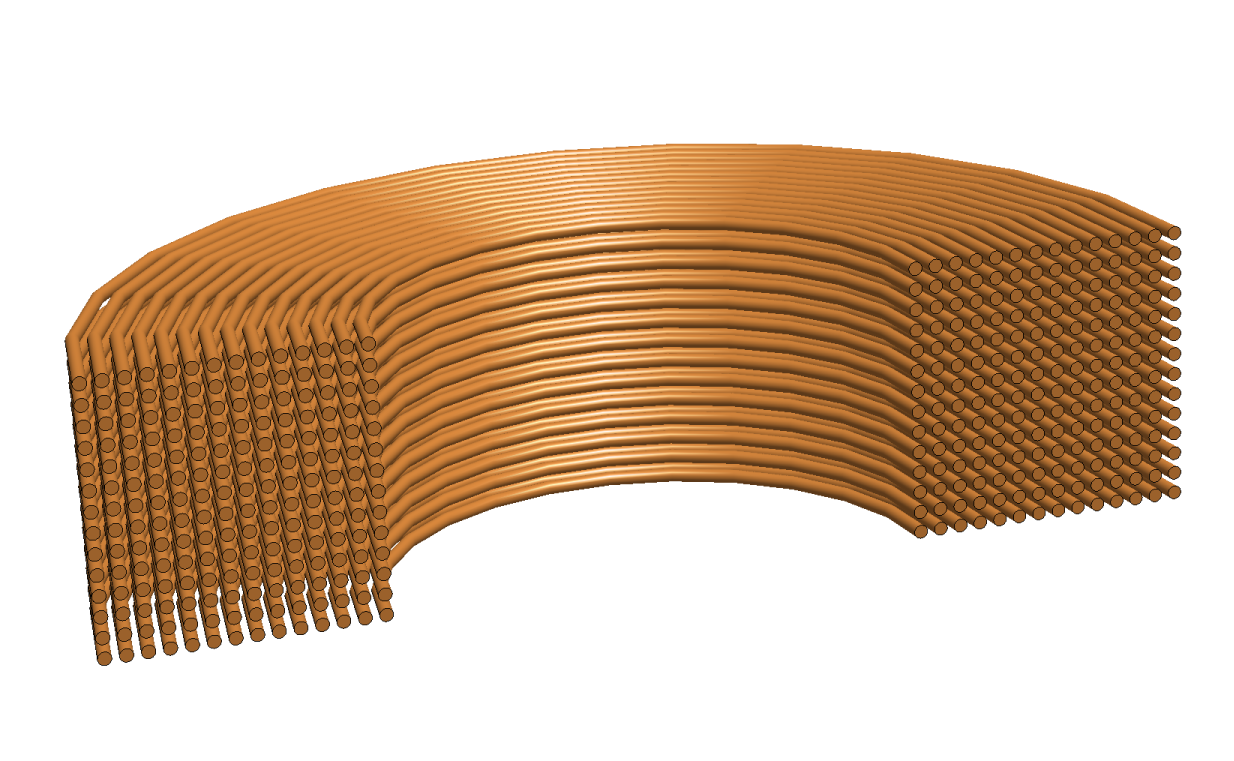 |
| Solid coil |
|
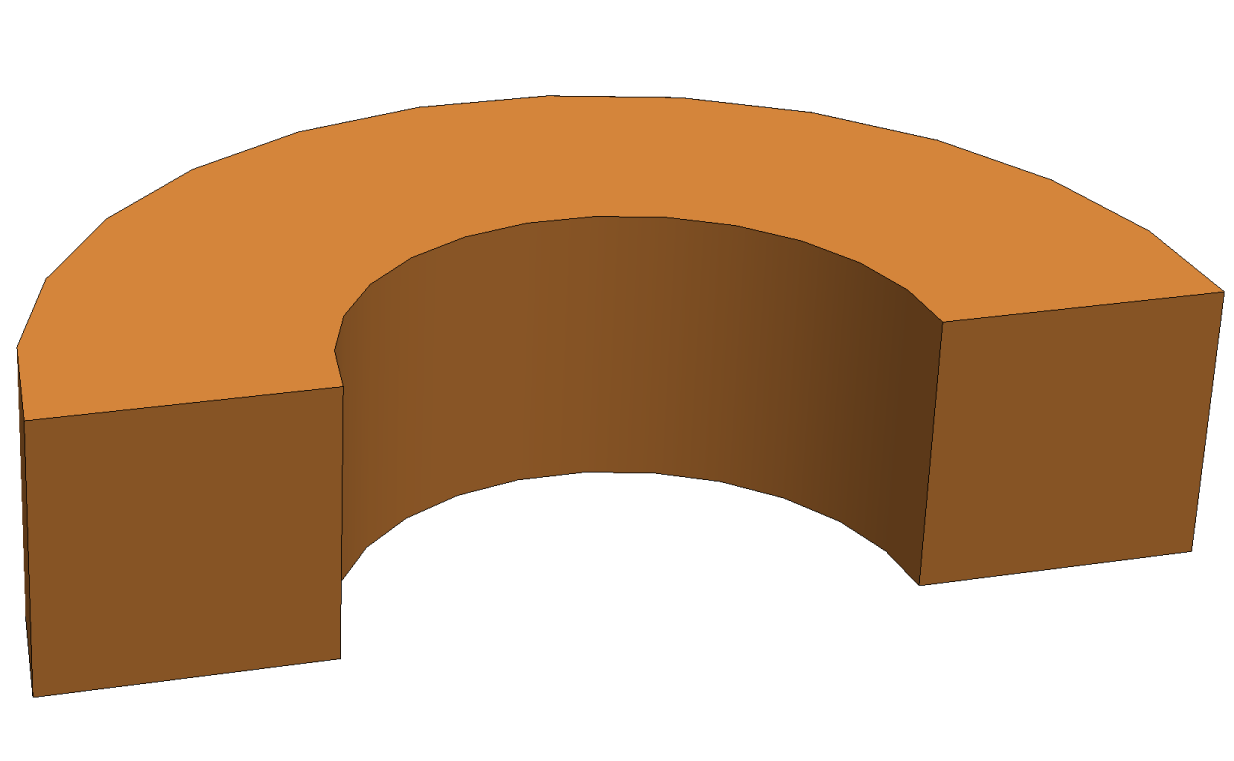 |
| Litz wire coil |
|
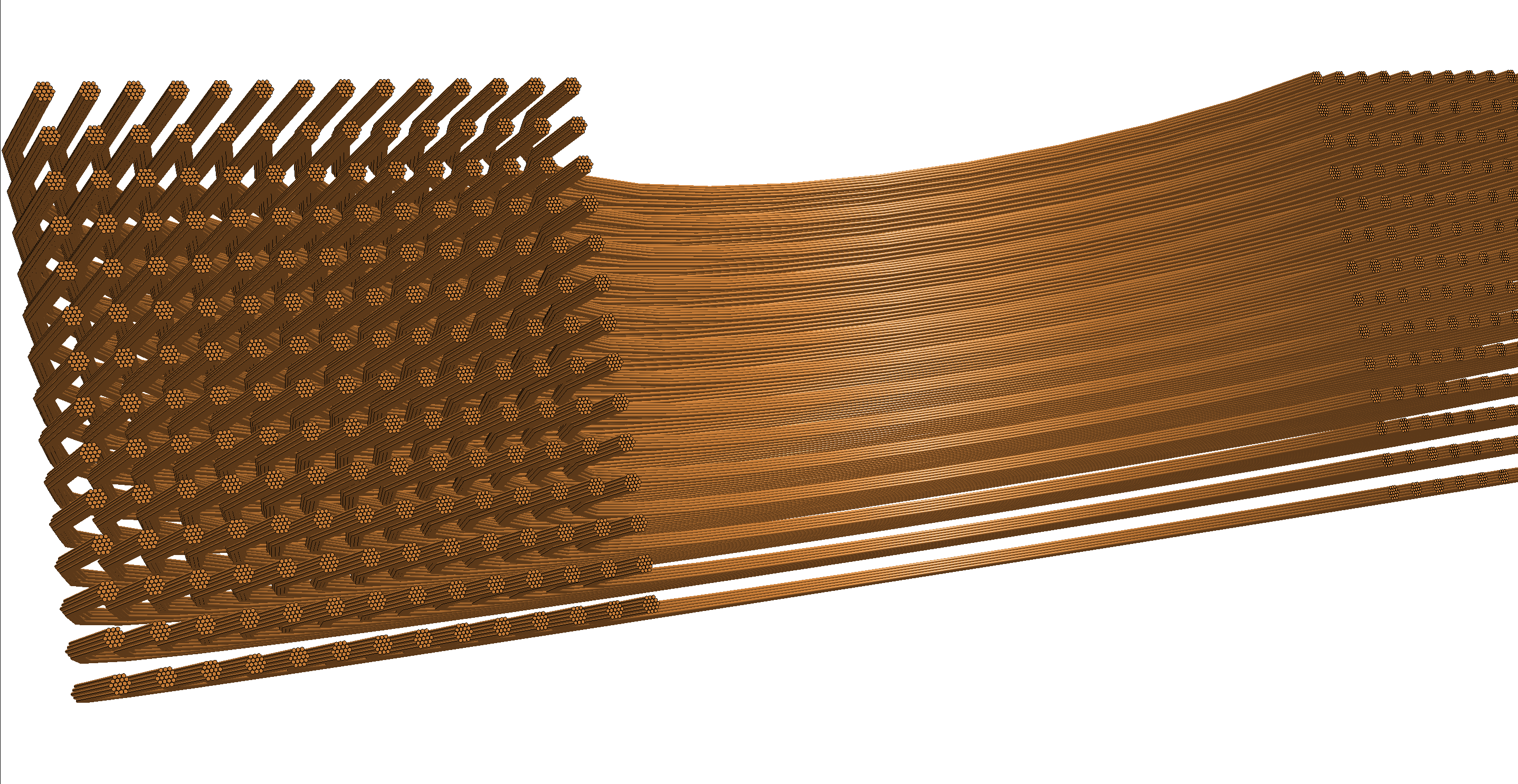 |
| Foil coil |
|
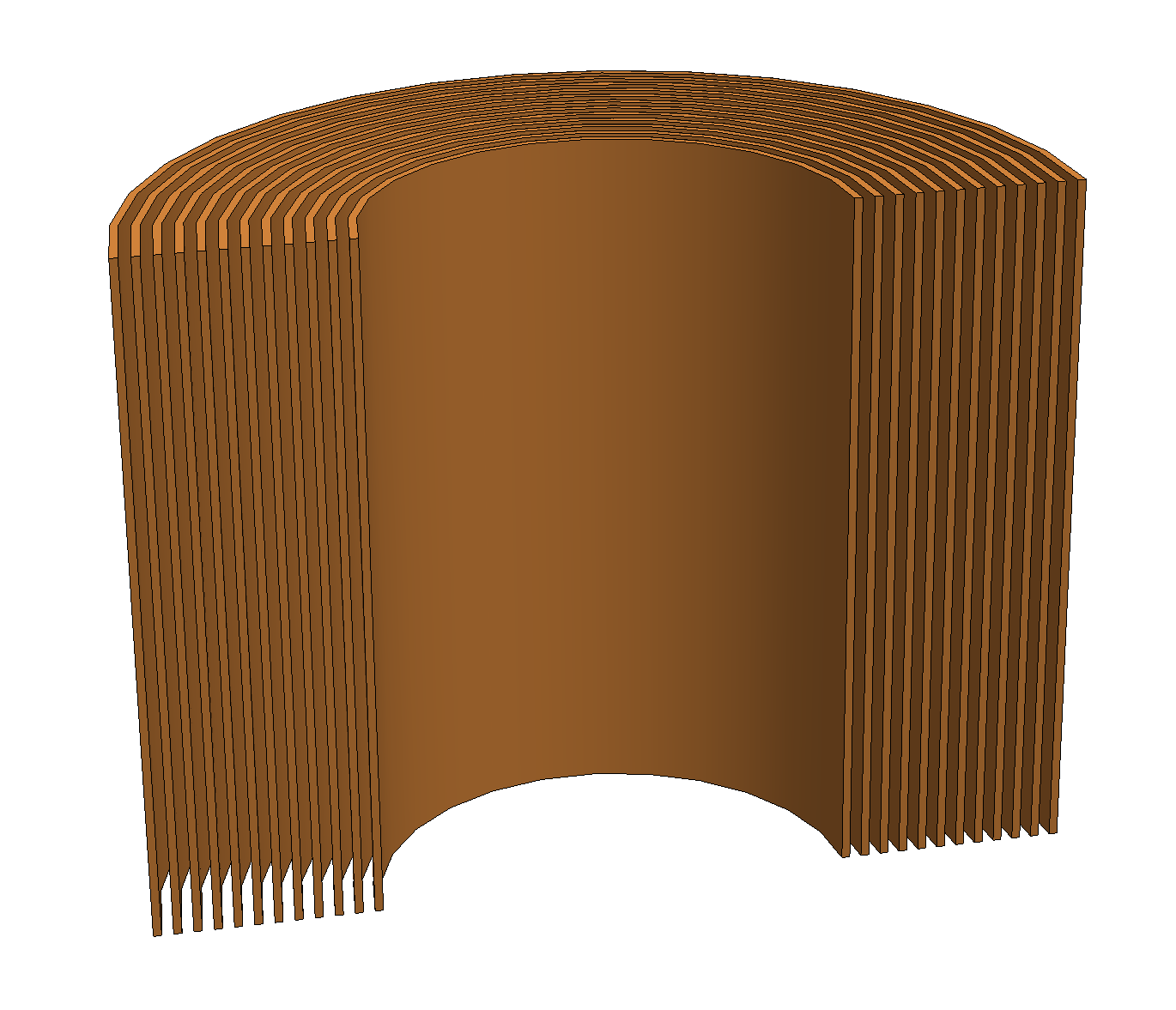 |
Coil Excitation¶
A coil is driven by an electrical source. It possesses intrinsic resistance and inductance, which produce ohmic losses and magnetic energy storage.
| Name | Description | Illustration |
|---|---|---|
| Current excitation | The coil current is prescribed directly. | 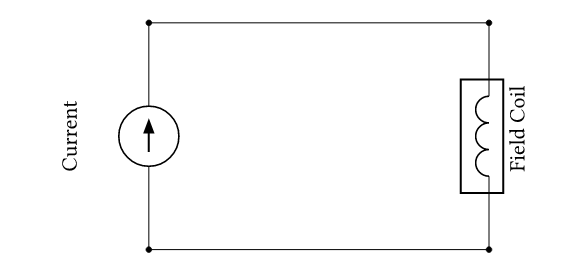 |
| Voltage excitation | A voltage is applied. Coil resistance and inductance determine the resulting current. | 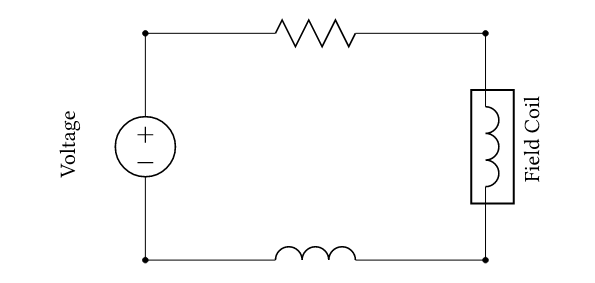 |
Reports¶
Available reports. Note that some are only available with the Time-Domain Magnetic Model.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Coil current | Scalar | Instantaneous current in the coil. |
| Coil resistance | Scalar | Returns the electrical resistance of the coil. |
| Flux linkage | Scalar | Total magnetic flux linked with the coil. |
| Magnetic Inductance | Symmetric matrix | Provides the self- and mutual inductances of all coils. |